Chapter 50 Managing financial risks
Forbidden, but useful, tools …
The graph below illustrates the high volatility of some parameters of importance for the profit and loss account of companies: exchange rate (dollar/euro), interest rate (Eonia), raw materials (copper) and services (freight rates).
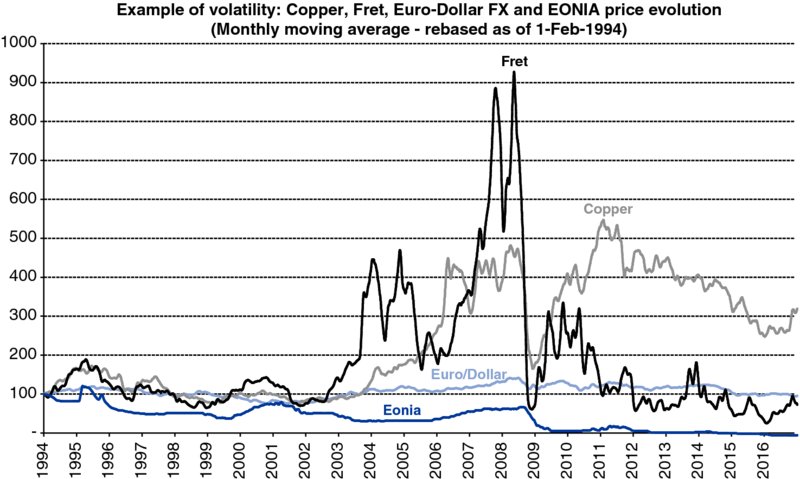
Source: Factset – copper spot price in $ per MT: London Metal Exchange – Fret price: Baltic Dry Index
Accordingly, investors, supervisory authorities and managers pay more and more attention to risk management. This has led to:
- management teams’ awareness of the importance of risk monitoring that leads to the setting up or the reinforcement of departments dedicated to risk management (internal audit, risk managers);
- increasing pressure from capital markets to show more transparency. Guidance on better governance hints at reinforcing the power of directors in the management of risks through the implementation of risk audit committees;
- a regulatory framework imposing communication on procedures to identify and assess risks for the firm and on strategy for management of those risks and its efficiency.
The evolution of risk management in recent years has consisted in increasingly segmenting risks and developing products that offer more accurate and flexible hedging for risk that in the past had not always been well assessed.
Section 50.1 Introduction to risk management
1.
Get Corporate Finance, 5th Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

