Appendix B
Matrix Theory: Related Topics
What Is a Matrix?
A matrix is an array of elements arranged in rows and columns. Matrix manipulations play a significant role in multivariate analysis, or pattern analysis.
If matrix A has m rows and n columns, then we say that matrix A is of size m × n. An example of 3 × 4 matrix is shown as follows:

Transpose of a Matrix
If the rows and columns of matrix A are interchanged, the resultant matrix is called the transpose of matrix A and is denoted by AT or A′. If A is of size m × n, then AT is of size n × m. The transpose of A is a 3 × 4 matrix and is shown as follows:
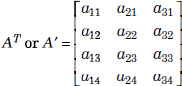
Square Matrix
If the number of rows and the number of columns of a matrix are the same, then that matrix is called a square matrix.
Determinant of a Matrix
The determinant is a characteristic number associated with a square matrix. The importance of the determinant can be realized when solving a system of linear equations using matrix algebra. The solution to the system of equations contains the inverse matrix term, which is obtained by dividing the adjoint matrix by the determinant. If the determinant is zero, then the solution does not exist.
Let us consider a 2 × 2 matrix, as follows:
The determinant of this matrix is a11a22 − a12a21.
Now let us consider a 3 × 3 ...
Get Competing with High Quality Data: Concepts, Tools, and Techniques for Building a Successful Approach to Data Quality now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

