Problems Between the Host and the Default Router
Imagine that you work as a customer support rep (CSR) fielding calls from users about problems. A user left a message stating that he couldn’t connect to a server. You could not reach him when you called back, so you did a series of pings from that host’s default router, using some of the problem isolation strategies described in Chapter 4. And at the end of those pings, you think the problem exists somewhere between the user’s device and the default router—for instance, between router R1 and host A, as shown in Figure 5-1.
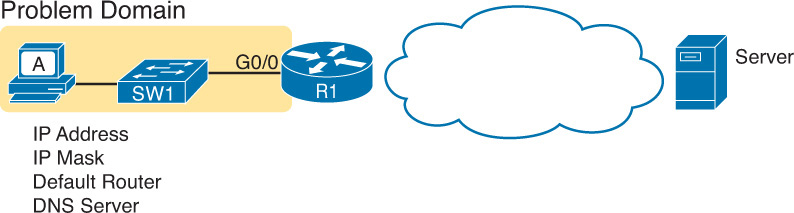
Figure 5-1 Focus of the Discussions in This Section of the Chapter
Get Cisco CCNA Routing and Switching ICND2 200-101 Official Cert Guide now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

