Chapter 6
The Third Law of Thermodynamics
6.a. The Nernst Heat Theorem
The first and second laws of thermodynamics have enabled us to tabulate enthalpies (sec. 3.a) and free energies (sec. 5.f) of substances. A similar tabulation of value of S0 is desirable. Entropy changes can be calculated (sec. 4.e.2). The entropy of one mol of any substance at a temperature T, and at a given pressure can be expressed as
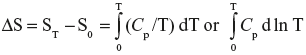
(sec. 4.e.2). Here S0 is the hypothetical entropy at absolute zero. If S0 is known, one can calculate the entropy of a substance at any temperature from heat capacity data. This chapter describes such attempts.
By using the Gibbs–Helmholtz ...
Get Chemical Thermodynamics now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

