IS-IS Addressing
CLNP uses a format of addressing, referred to as the network service access point (NSAP) address, to identify individual nodes on a network. Figure 11-4 illustrates the NSAP packet. The NSAP address has a maximum size of 160 bits (20 bytes) and is composed of the following major parts:
The initial domain part (IDP)— Made of a 1-byte authority and format identifier (AFI) and a variable-length initial domain identifier (IDI)
The domain specific part (DSP)— Composed of fields such as the area ID, system ID, and the N-selector
Figure 11-4. The NSAP Packet
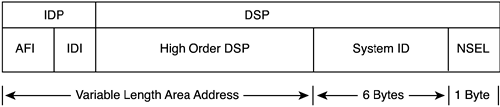
The Simplified NSAP Format
The NSAP format was designed with a hierarchical ...
Get CCIE Practical Studies: Security (CCIE Self-Study) now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

