Name
slice class — Slice of an array
Synopsis
class slice { public: slice( ); slice(size_t, size_t, size_t); size_t start( ) const; size_t size( ) const; size_t stride( ) const; };
The slice class describes a
slice of a valarray. A slice is a
subset of the elements of a valarray at periodic indices. The slice
has a starting index, a size, and a stride, in which the stride is
the index interval. Figure
13-28 depicts slice(1,3,4)
of a valarray.
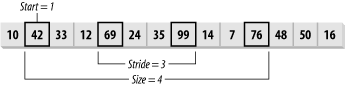 |
Use the subscript operator to take a slice of a valarray. You can assign a valarray to a slice, in which the
righthand side of the assignment must have the same size as the size
of the slice. You can also convert the slice to a valarray, which copies only those elements
of the slice to the new valarray.
When you take a slice of a valarray, the result is a slice_array object, but the slice_array type is mostly transparent to
the programmer. See slice_array
later in this section for details.
You can use a slice to treat a valarray as a two-dimensional matrix. A
slice can specify a row or column of the matrix. For an n × m matrix, row r is slice(r*m,
m, 1), and column c is slice(c, n, m), as you can see in Example 13-46.
Example
template<typename T> class matrix2D { public: matrix2D(std::size_t rows, std::size_t columns) : rows_(rows), cols_(columns), data_(rows * columns) {} std::size_t ...Get C++ In a Nutshell now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

