16
Straight Lines
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
After studying this chapter, the student will be able to understand:
- Concept of concurrent lines and its theorems
- Perpendicular distance from the point to the line
- Perpendicular distance between two parallel lines
- Equation of bisector of angle between two lines
INTRODUCTION
CONCURRENT LINES
If more than two lines intersect in exactly one common point then they are said to be concurrent lines.
Theorem 1
The necessary and sufficient conditions for three distinct lines:
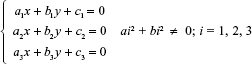
The conditions for three distinct lines to be concurrent are:
Theorem 2
If axx + bxy + Cj = 0; a2x + b2y + c2 = 0 (ai2 + bi2
Get Business Mathematics now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

