10.5 ADAPTIVE TRANSFORM ACOUSTIC CODING (ATRAC)
The ATRAC algorithm, developed by Sony for use in its rewriteable Mini-Disc system [Yosh94], combines subband and transform coding to achieve nearly CD-quality coding of 44.1 kHz 16-bit PCM input data at a bit rate of 146 kb/s per channel [Tsut98]. Using a tree-structured QMF analysis bank (Section 6.5), the ATRAC encoder (Figure 10.24) first splits the input signal into three subbands of 0–5.5 kHz, 5.5–11 kHz, and 11–22 kHz. Like MPEG-1 layer III, the ATRAC QMF bank is followed by signal-adaptive MDCT analysis in each subband. Next, a window-switching scheme is employed that can be summarized as follows. During steady-state input periods, high-resolution spectral analysis is attained using 512 sample blocks (11.6 ms). During input attack or transient periods, short block sizes of 1.45 ms in the high-frequency band and 2.9 ms in the low- and mid-frequency bands are used for pre-echo cancellation.
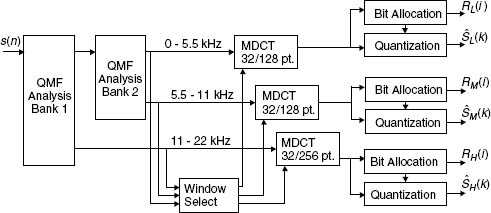
Figure 10.24. Sony ATRAC (embedded in MiniDisc, SDDS).
After MDCT analysis, spectral components are clustered into 52 nonuniform subbands (block floating units or BFUs) according to critical band spacing. The BFUs are block-companded, quantized, and encoded according to a psychoacoustically derived bit allocation. For each analysis frame, the ATRAC encoder transmits quantized MDCT coefficients, subband window lengths, BFU scale-factors, and ...
Get Audio Signal Processing and Coding now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

