3.2 DENSITY FUNCTIONS AND QUANTIZATION
In this section, we discuss the characterization of a random process in terms of its probability density function (PDF). This approach will help us derive the quantization noise equations for different quantization schemes. A random process is characterized by its PDF, which is a non-negative function, p(x), whose properties are
![]()
and
![]()
From the above equations, it is evident that the PDF area from x1 to x2 is the probability that the random variable X is observed in this range. Since X lies somewhere in [−∞, ∞], the total area under p(x) is one. The mean and the variance of the random variable X are defined as
![]()
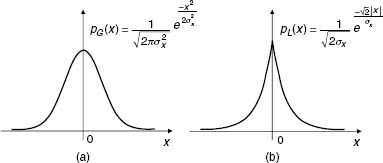
Figure 3.2. (a) The Gaussian PDF and (b) The Laplacian PDF.
![]()
Note that the expectation is computed either as a weighted average (3.3) or under ergodicity assumptions as a time average (Chapter 2, Eq. 2.54). PDFs are useful in the design of optimal signal quantizers as they can be used to determine the assignment of optimal quantization levels. ...
Get Audio Signal Processing and Coding now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

