Chapter 9Stochastic Correlation
Stochastic correlation models may provide a more realistic approach to the pricing and hedging of certain types of exotic derivatives, such as worst-of and best-of options and correlation swaps and correlation options. In this chapter, we review various types of stochastic correlation models and propose a framework for the pricing of realized correlation derivatives that is consistent with variance swap markets.
9.1 Stochastic Single Correlation
Consider the following general model framework for two assets S(1) and S(2):
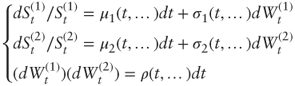
where μ's are instant drift coefficients, σ's are instant volatility coefficients, and ρ is the instant correlation coefficient between the driving Brownian motions W's. Here all the coefficients may be stochastic, and we focus on ρ.
There are some simple ways to make ρ stochastic and comprised between −1 and 1; for example, take ![]() where Z is an independent Brownian motion. The dynamics of dρt may then be found by means of the Ito-Doeblin theorem. One issue with this approach is that the parameters may not be very intuitive.
where Z is an independent Brownian motion. The dynamics of dρt may then be found by means of the Ito-Doeblin theorem. One issue with this approach is that the parameters may not be very intuitive.
A better approach is to specify diffusion dynamics for ρ and examine the Feller conditions at bounds −1 and 1 (see Section 2.4.2.2). A popular process here is the affine Jacobi process, also known as a Fischer-Wright ...
Get Advanced Equity Derivatives: Volatility and Correlation now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

