Chapter 3Fair Valuation – Credit and Debit Valuation Adjustments
This chapter covers the application of IFRS 13 Fair Value Measurement to the valuation of financial instruments and in particular credit and debit valuation adjustments (CVAs and DVAs).
3.1 FAIR VALUATION – OVERVIEW OF IFRS 13
IFRS 13 defines fair value, provides principles-basedguidance on how to measure fair value, and requires information about those fair value measurements to be disclosed in the financial statements (see Figure 3.1). IFRS 13 applies when another IFRS requires or permits the measurement or disclosure of fair value (e.g., IFRS 9), or a measure that is based on fair value, except to the following standards:
- share-based payment transactions within the scope of IFRS 2 Share-Based Payment;
- leasing transactions within the scope of IAS 17 Leases; and
- measurements that have some similarities to fair value but are not fair value, such as net realisable value in IAS 2 Inventories or value in use in IAS 36 Impairment of Assets.
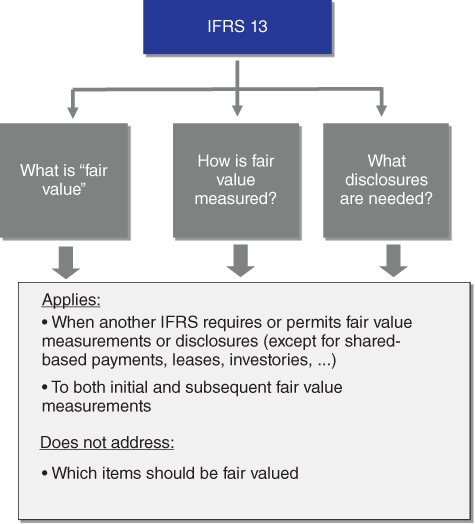
Figure 3.1 IFRS 13 summary.
The disclosures required by this IFRS are not required for the following:
- plan assets measured at fair value in accordance with IAS 19 Employee Benefits;
- retirement benefit plan investments measured at fair value in accordance with IAS 26 Accounting and Reporting by Retirement Benefit Plans; and
- impaired assets measured at fair value less costs ...
Get Accounting for Derivatives: Advanced Hedging under IFRS 9, 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

