16.3. Encoding a Database
When a database is secured as described in Shared-Level Security, the security only applies to attempts to access the database using the Microsoft Jet Engine. Any attempt to open the database using ODBC, for example, from Excel will request the database password. However, if the MDB file is opened using a non-Jet access method, such as through Windows Notepad, the data can be viewed.
If it is necessary to prevent anyone from analyzing the information in a database using a non-Jet access method, you should encode the database. This will encrypt the information contained in the database to prevent unauthorized access to the data through other means.
When you encode a database, you encode to a new database and the original database is saved without encoding.
Figure 16.6. Figure 16-6
16.3.1. Creating an Encoded Database
To encode a database, the database must be opened in Exclusive mode as described earlier and depicted in Figure 16-3.
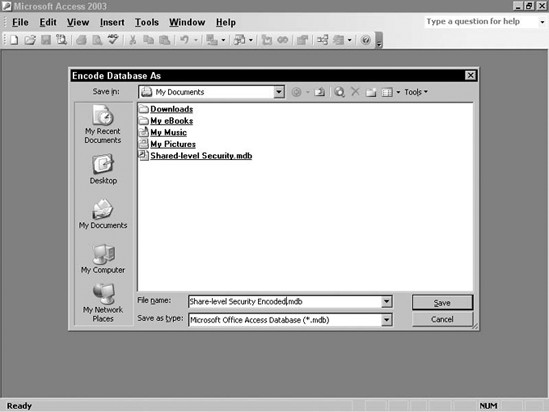
Select Tools | Security | Encode/Decode Database... from the menu to display the Encode Database As dialog box shown in Figure 16-6.
Then select a location to store the encoded database and enter a name for it. Click Save to create the encoded database.
After you have encoded the database, either delete the original database or move it to a secured location where it has adequate protection from unauthorized users and from ...
Get Access 2003 VBA Programmer's Reference now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

