11 IoT Security
Mehrnoosh Monshizadeh1,2 and Vikramajeet Khatri1
1 Nokia Bell Labs, Finland
2 Aalto University, Finland
11.1 Introduction
Mobile network operators should meet connectivity requirements for new applications, which will be released in coming years. Comparing to Long Term Evolution (LTE) networks, 5G will offer increased data rate, reduced end‐to‐end latency, and improved coverage, which are essential factors for many Internet of Things (IoT) applications such as unmanned cars, smart cities and intelligent transportation systems. Figure 11.1 shows the 5G use cases and requirements [1].
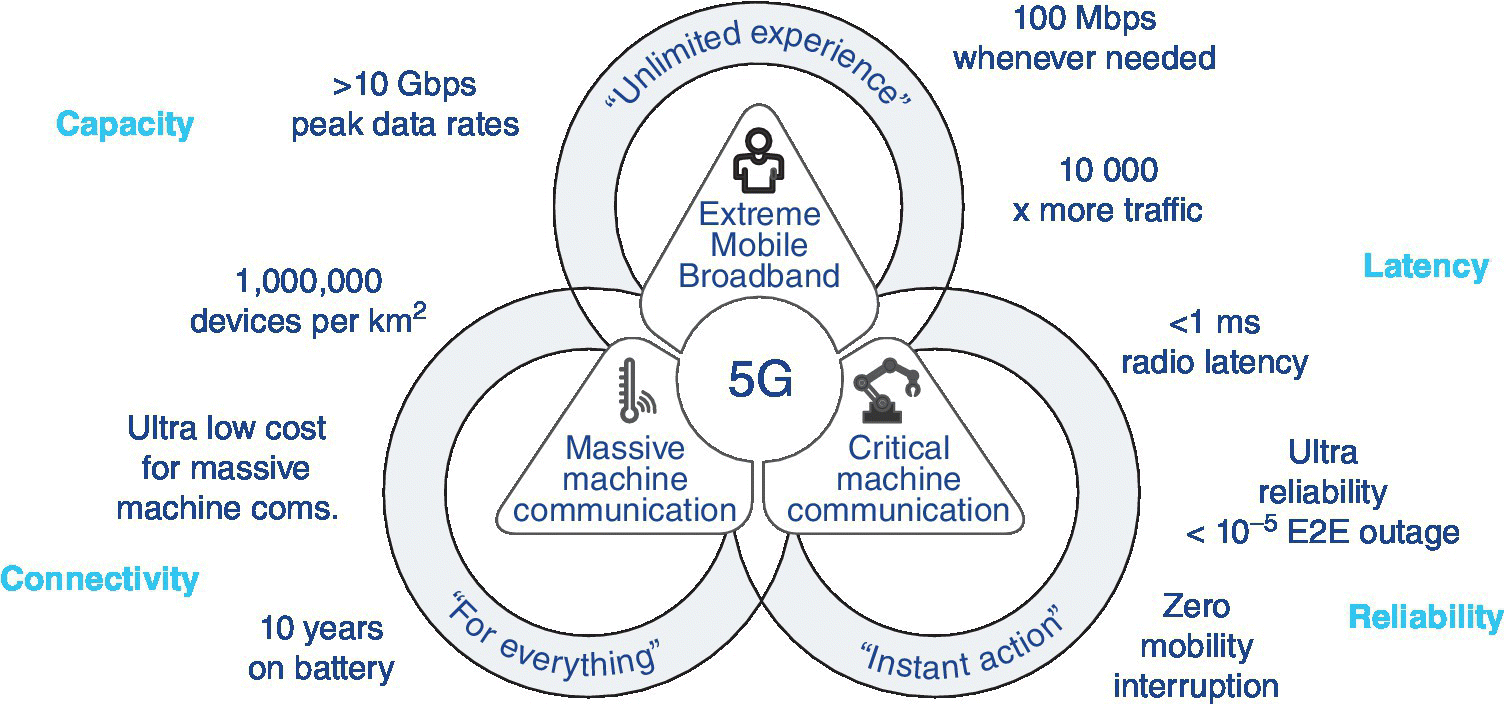
Figure 11.1 5G use cases and requirements [1].
The existing technologies of cloud computing, IoT, and wireless controlled robots combine to produce a new variant called Cloud Robotics. Cloud Robotics uses the big data techniques and computing power of the cloud along with the connectivity provided by 5G, LTE and other wireless technologies to control the actions of wireless robots. We shall refer to this technology as Mobile Cloud Robot (MCR), where the robot‐cloud connectivity is provided by mobile networks. This technology has the mutual attention of telecommunication vendors as well as different industries, including manufacturing, medicine and agriculture.
Because of the operational characteristics of resource sharing and a centralized controller, MCR can act as a potential ...
Get A Comprehensive Guide to 5G Security now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

