Stacking Order
In the visual formatting model for tables , the various table elements are understood to occupy separate superimposed layers. These are used to determine which backgrounds are visible. Elements are transparent by default, allowing the backgrounds of the layers “below” to show through. A background applied to a particular element will be visible if all the elements “above” it are transparent.
The stacking order for table element layers is, from “top” to “bottom”: cell, row, row group, column, column group, table, as shown in the diagram in Figure 22-3.
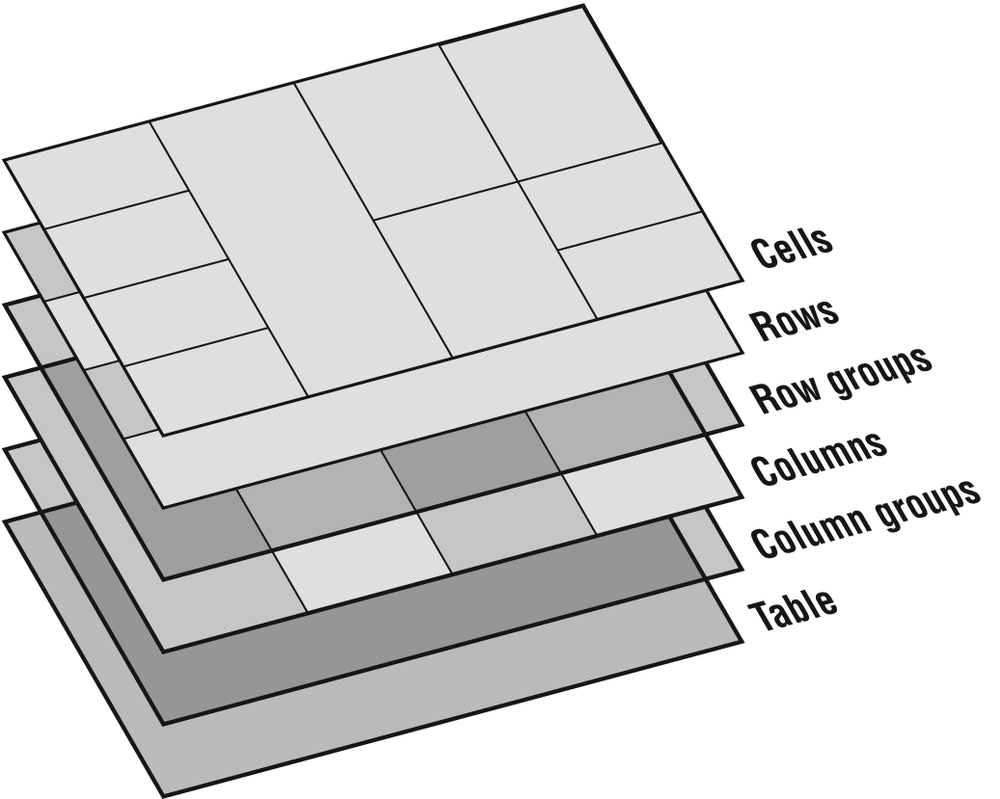
Figure 22-3. Table layer order
Or in other words, applying a background color in a cell will paint over any backgrounds provided in rows, row groups, and so on. This system is similar to the way in which color attributes in HTML table cells (td) override row settings (tr), which in turn override settings at the table level (table). One significant aspect of the CSS model is that table rows and row groups are given precedence over columns and column groups.
Get Web Design in a Nutshell, 3rd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

