Introduction to Flash
Macromedia Flash utilizes vector-based technology to deliver interactive real-time animation and sound over slow modem connections. Unlike Director, Flash was developed specifically for the Web. Mathematical algorithms enable Flash to stream high-resolution vector-based graphics instantaneously. Figure 9-2 shows vector artwork in the main Flash authoring window combined with bitmap images.
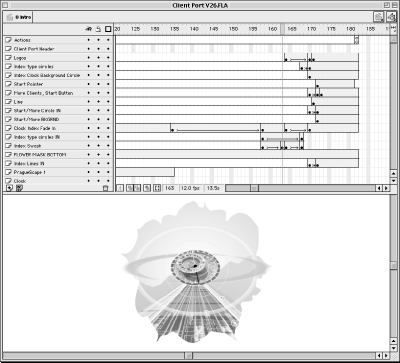
Figure 9-2. Flash 4 scene window
Flashâs primary advantage over Shockwave is that its extremely small vector animations download quickly and play at real-time speeds, allowing more bandwidth to be allocated to audio content. For this reason, Flash is generally regarded as one of the few interactive multimedia formats that really works over limited bandwidths. Flash has expanded its user base even more since Macromedia declared the Flash file format an open Internet standard. In 2000, Adobe will release a product, LiveMotion, which writes Flash files as well as many other files.
The Flash plug-in is also much smaller than the Director Shockwave plug-in. Director Shockwave has the additional overhead of the Lingo interpreter and streaming decoder. Macromedia was determined to retain the Flash plug-inâs optimal 150 KB file size. So despite the fact that Lingo and SWA decompression capabilities would enhance Flash, Macromedia did not incorporate them into Flash. Instead, Flash ...
Get Designing Web Audio & CD-ROM now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

