Chapter 13. Streams and I/O
This chapter describes the fundamental types for input and output in .NET, with emphasis on the following topics:
The .NET stream architecture and how it provides a consistent programming interface for reading and writing across a variety of I/O types
Manipulating files and directories on disk
Isolated storage and its role in segregating data by program and user
This chapter concentrates on the types in the System.IO namespace, the home of lower-level I/O
functionality. The .NET Framework also provides higher-level I/O
functionality in the form of SQL connections and commands, LINQ to SQL and
LINQ to XML, Web Services, Remoting, and Windows Communication
Foundation.
Stream Architecture
The .NET stream architecture centers on three concepts: backing stores, decorators, and adapters, as shown in Figure 13-1.
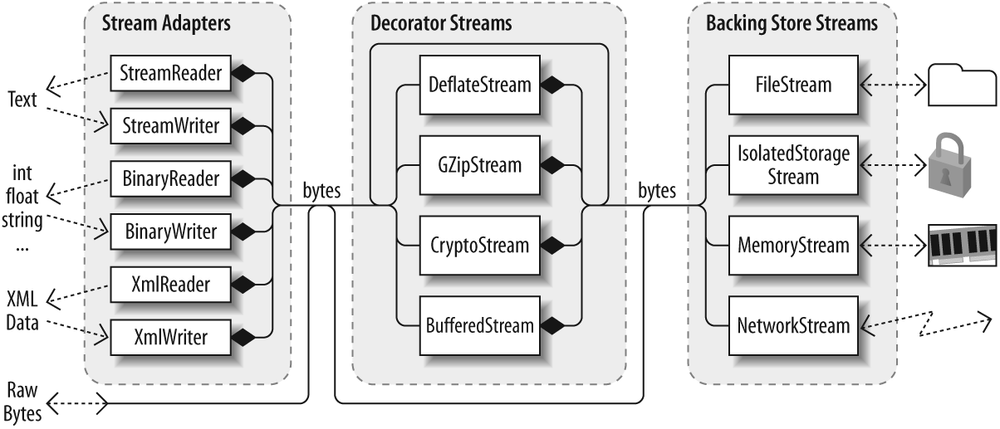
A backing store is the endpoint that makes input and output useful, such as a file or network connection. Precisely, it is either or both of the following:
A source from which bytes can be sequentially read
A destination to which bytes can be sequentially written
A backing store is of no use, though, unless exposed to the programmer. A stream is the standard .NET class for this purpose; it exposes a standard set of methods for reading, writing, and positioning. Unlike an array, where all the backing data exists in memory at once, ...
Get C# 3.0 in a Nutshell, 3rd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

